Created by: karen.west
Number of Blossarys: 1
 English (EN)
English (EN) Greek (EL)
Greek (EL) Czech (CS)
Czech (CS) Chinese, Simplified (ZS)
Chinese, Simplified (ZS) Bulgarian (BG)
Bulgarian (BG) Thai (TH)
Thai (TH) Albanian (SQ)
Albanian (SQ) Polish (PL)
Polish (PL) Japanese (JA)
Japanese (JA) Arabic (AR)
Arabic (AR) Croatian (HR)
Croatian (HR)
 Romanian (RO)
Romanian (RO) Macedonian (MK)
Macedonian (MK) Spanish (ES)
Spanish (ES) Serbian (SR)
Serbian (SR) Indonesian (ID)
Indonesian (ID) Russian (RU)
Russian (RU) French (FR)
French (FR) Turkish (TR)
Turkish (TR) Italian (IT)
Italian (IT) Spanish, Latin American (XL)
Spanish, Latin American (XL) Hungarian (HU)
Hungarian (HU) Portuguese, Brazilian (PB)
Portuguese, Brazilian (PB) Malay (MS)
Malay (MS) Korean (KO)
Korean (KO) Slovenian (SL)
Slovenian (SL) Dutch (NL)
Dutch (NL) Lithuanian (LT)
Lithuanian (LT) English, UK (UE)
English, UK (UE) Chinese, Hong Kong (ZH)
Chinese, Hong Kong (ZH) French, Canadian (CF)
French, Canadian (CF) Estonian (ET)
Estonian (ET)
 Greek (EL)
Greek (EL) Czech (CS)
Czech (CS) Chinese, Simplified (ZS)
Chinese, Simplified (ZS) Bulgarian (BG)
Bulgarian (BG) Thai (TH)
Thai (TH) Albanian (SQ)
Albanian (SQ) Polish (PL)
Polish (PL) Japanese (JA)
Japanese (JA) Arabic (AR)
Arabic (AR) Croatian (HR)
Croatian (HR)
 Romanian (RO)
Romanian (RO) Macedonian (MK)
Macedonian (MK) Spanish (ES)
Spanish (ES) Serbian (SR)
Serbian (SR) Indonesian (ID)
Indonesian (ID) Russian (RU)
Russian (RU) French (FR)
French (FR) Turkish (TR)
Turkish (TR) Italian (IT)
Italian (IT) Spanish, Latin American (XL)
Spanish, Latin American (XL) Hungarian (HU)
Hungarian (HU) Portuguese, Brazilian (PB)
Portuguese, Brazilian (PB) Malay (MS)
Malay (MS) Korean (KO)
Korean (KO) Slovenian (SL)
Slovenian (SL) Dutch (NL)
Dutch (NL) Lithuanian (LT)
Lithuanian (LT) English, UK (UE)
English, UK (UE) Chinese, Hong Kong (ZH)
Chinese, Hong Kong (ZH) French, Canadian (CF)
French, Canadian (CF) Estonian (ET)
Estonian (ET)
Generalni pojam za celiju bez sposobnosti za samoobnavljanjem sto doprinosi formiranju tkiva. U nekim slucajevima prozivode se maticne celije tkiva.
Generalni pojam za celiju bez sposobnosti za samoobnavljanjem sto doprinosi formiranju tkiva. U nekim slucajevima prozivode se maticne celije tkiva.
Uzgajanje celija u laboratorijskoj posudi za eksperimentalno istrazivanje. Celije su uzgajane u rastvoru, ili medijumu, koji sadrzi hranljive sastojke i faktore rasta. Razliciti faktori se mogu dodati medijumu da bi se podstakle promene u ponasanju celija.
Uzgajanje celija u laboratorijskoj posudi za eksperimentalno istrazivanje. Celije su uzgajane u rastvoru, ili medijumu, koji sadrzi hranljive sastojke i faktore rasta. Razliciti faktori se mogu dodati medijumu da bi se podstakle promene u ponasanju celija.
Populacija celija koje nose iste gene, uzgajane u laboratoriji kroz mnogstruke cikluse rasta i deobe kroz mnoge generacije celija.
Populacija celija koje nose iste gene, uzgajane u laboratoriji kroz mnogstruke cikluse rasta i deobe kroz mnoge generacije celija.
Proces u kome maticne celije sticu osobine specijalizovanih odraslih celija kao sto su srcane, mozdane ili celije pankreasa.
Proces u kome maticne celije sticu osobine specijalizovanih odraslih celija kao sto su srcane, mozdane ili celije pankreasa.
Jdena od dve ili vise celija koje se formiraju u toku deobe jedne jedine celije.
Jdena od dve ili vise celija koje se formiraju u toku deobe jedne jedine celije.
Maticna celija od koje nastaju svi tipovi celija krvi.
Maticna celija od koje nastaju svi tipovi celija krvi.
Maticna celija od koje nastaju svi tipovi celija krvi.
Maticna celija od koje nastaju svi tipovi celija krvi.
Rekonstrukcija obolelog ili povredjenog tkiva aktivacijom sopstvenih celija ili transplantacijom.
Rekonstrukcija obolelog ili povredjenog tkiva aktivacijom sopstvenih celija ili transplantacijom.
Sposobnost maticne celije da se deli i da proizvodi kopije same sebe nedefinisani period vremena. Ovo je definisuce svojstvo maticnih celija.
Sposobnost maticne celije da se deli i da proizvodi kopije same sebe nedefinisani period vremena. Ovo je definisuce svojstvo maticnih celija.
Sposobnost maticne celije da se deli i prozivodi kopije same sebe nedefinisani period vremena. Ovo je definisuce svojstvo maticnih celija.
Sposobnost maticne celije da se deli i prozivodi kopije same sebe nedefinisani period vremena. Ovo je definisuce svojstvo maticnih celija.
Maticne celije koje rastu u celijskoj kulturi vise od sest meseci bez diferenciranja i koje su genetski normalne.
Maticne celije koje rastu u celijskoj kulturi vise od sest meseci bez diferenciranja i koje su genetski normalne.
Celija koja moze kontinuirano prozivoditi neizmenjene celije cerke i koja takodje ima sposobnost da prozivodi celije cerke koje imaju razlicita, vise ogranicavajuca svojstva.
Celija koja moze kontinuirano prozivoditi neizmenjene celije cerke i koja takodje ima sposobnost da prozivodi celije cerke koje imaju razlicita, vise ogranicavajuca svojstva.
Tehnika kojom se oplodjuje jajna celija van tela. Korisiti se za vestacku oplodnju, oplodjena jajna celija se usadjuje u matericu otprilike nakon tri do cetiri dana celijske deobe u svrhu da se razvije u bebu. Za upotrebu u istrazivanju, oplodjena jajna celija se odrzava u celijskoj kulturi dok se ne razvije u blastocistu do otprilike petog dana celijske deobe kada se mogu uzeti maticne celije.
Tehnika kojom se oplodjuje jajna celija van tela. Korisiti se za vestacku oplodnju, oplodjena jajna celija se usadjuje u matericu otprilike nakon tri do cetiri dana celijske deobe u svrhu da se razvije u bebu. Za upotrebu u istrazivanju, oplodjena jajna celija se odrzava u celijskoj kulturi dok se ne razvije u blastocistu do otprilike petog dana celijske deobe kada se mogu uzeti maticne celije.
Proces koji se desava u laboratoriji (npr. u celijskoj kulturi).
Proces koji se desava u laboratoriji (npr. u celijskoj kulturi).
Funkcionalna celija jetre. Hepatociti proizvode enzime za detoksikaciju metabolickih otpadnih produkata, sintetisu proteine krvne plazme, proizvode zuc i pomazu u kontroli nivoa glukoze u krvi u okviru uskih granica.
Funkcionalna celija jetre. Hepatociti proizvode enzime za detoksikaciju metabolickih otpadnih produkata, sintetisu proteine krvne plazme, proizvode zuc i pomazu u kontroli nivoa glukoze u krvi u okviru uskih granica.
An early stage embryo of about 100 cells that has not yet implanted into the womb. The blastocyst is a sphere made up of an outer layer of cells, a fluid-filled cavity and cluster of cells inside called the inner cell mass. The blastocyst develops after cleavage and prior to implantation at approximately five days. Further reproductive development occurs only if the blastocyst is successfully implanted in the uterus.
An early stage embryo of about 100 cells that has not yet implanted into the womb. The blastocyst is a sphere made up of an outer layer of cells, a fluid-filled cavity and cluster of cells inside called the inner cell mass. The blastocyst develops after cleavage and prior to implantation at approximately five days. Further reproductive development occurs only if the blastocyst is successfully implanted in the uterus.
A cell produced during cleavage of a fertilized egg.
A cell produced during cleavage of a fertilized egg.
An early stage embryo of about 100 cells that has not yet implanted into the womb. The blastocyst is a sphere made up of an outer layer of cells, a fluid-filled cavity and cluster of cells inside called the inner cell mass. The blastocyst develops after cleavage and prior to implantation at approximately five days. Further reproductive development occurs only if the blastocyst is successfully implanted in the uterus.
An early stage embryo of about 100 cells that has not yet implanted into the womb. The blastocyst is a sphere made up of an outer layer of cells, a fluid-filled cavity and cluster of cells inside called the inner cell mass. The blastocyst develops after cleavage and prior to implantation at approximately five days. Further reproductive development occurs only if the blastocyst is successfully implanted in the uterus.
A research study in human subjects to answer specific questions about vaccines or new therapies or new ways of using known treatments. Clinical trials are used to determine whether new drugs or treatments are both safe and effective. Trials take place in four phases: Phase I tests a new drug or treatment in a small group; Phase II expands the study to a larger group of people; Phase III expands the study to an even larger group of people; and Phase IV takes place after the drug or treatment has been licensed and marketed.
A research study in human subjects to answer specific questions about vaccines or new therapies or new ways of using known treatments. Clinical trials are used to determine whether new drugs or treatments are both safe and effective. Trials take place in four phases: Phase I tests a new drug or treatment in a small group; Phase II expands the study to a larger group of people; Phase III expands the study to an even larger group of people; and Phase IV takes place after the drug or treatment has been licensed and marketed.
To create a copy. “Therapeutic cloning” creates a line of stem cells genetically identical to the originating cell for use in research. “Reproductive cloning” creates an organism genetically identical to the organism providing the originating cell.
To create a copy. “Therapeutic cloning” creates a line of stem cells genetically identical to the originating cell for use in research. “Reproductive cloning” creates an organism genetically identical to the organism providing the originating cell.
The developing human organism (a group of cells) that arise from a fertilized egg (after merging of egg and sperm). An embryo does have the potential to become a complete organism. The embryonic stage ends at eight weeks of development.
The developing human organism (a group of cells) that arise from a fertilized egg (after merging of egg and sperm). An embryo does have the potential to become a complete organism. The embryonic stage ends at eight weeks of development.
A developing human from the eighth week of gestation to birth.
A developing human from the eighth week of gestation to birth.
The functional cell type of the liver. Hepatocytes make enzymes for detoxifying metabolic waste, synthesise proteins for the blood plasma, produce bile and help control blood sugar levels within narrow limits.
The functional cell type of the liver. Hepatocytes make enzymes for detoxifying metabolic waste, synthesise proteins for the blood plasma, produce bile and help control blood sugar levels within narrow limits.
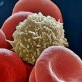
A type of white blood cell and a versatile part of the immune system. Constantly on patrol, macrophages can find and kill many different kinds of bacteria. They are usually the first responders to any invasion of the body.
A type of white blood cell and a versatile part of the immune system. Constantly on patrol, macrophages can find and kill many different kinds of bacteria. They are usually the first responders to any invasion of the body.
The oval spongy structure in the uterus from which the fetus derives its nourishment and oxygen. The placenta develops from the outer cell layer of the blastocyst, called the trophoblast.
The oval spongy structure in the uterus from which the fetus derives its nourishment and oxygen. The placenta develops from the outer cell layer of the blastocyst, called the trophoblast.
Cells from the body other than sperm or egg cells.
Cells from the body other than sperm or egg cells.
A type of white blood cell and a versatile part of the immune system. Constantly on patrol, macrophages can find and kill many different kinds of bacteria. They are usually the first responders to any invasion of the body.
A type of white blood cell and a versatile part of the immune system. Constantly on patrol, macrophages can find and kill many different kinds of bacteria. They are usually the first responders to any invasion of the body.
Any of the cells of a plant or animal other than germ cells (reproductive cells)
Any of the cells of a plant or animal other than germ cells (reproductive cells)
A single cell resulting from the fusion of male and female gametes (sperm and egg) at fertilization.
A single cell resulting from the fusion of male and female gametes (sperm and egg) at fertilization.